China’s attention reaches as far as the remote Svanbard Islands

The remote archipelago of Svalbard, a frozen frontier twice the size of Belgium, has become the unlikely center of international intrigue. As the ice retreats, revealing potential riches and strategic advantages, an unexpected player has entered the Arctic chessboard: China.
The Asian giant has recently turned its gaze towards the remote Norwegian Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, joining Russia, and is showing strong interest in this frozen frontier.
With China, Russia and even Turkey intensifying their focus on Svalbard, tensions in the Arctic are heating up. For Norway, China's new interest is more than just a curiosity: it is a serious 'national security concern'.
The Dragon's Arctic Ambition
Despite being thousands of kilometers from the Arctic Circle, China has boldly declared itself a “quasi-Arctic state.”
This bold statement, made in his 2018 Arctic policy, raised eyebrows throughout the international community. China isn't just talking about its Arctic ambitions, it's actively pursuing them right on the frozen terrain of Svalbard.
Last week, a Chinese delegation, including members of the China Arctic and Antarctic Administration (CAA) and the China Polar Research Institute (PRIC), made a significant move by visiting the Russian science center in Barentsburg, in Svalbard.
This visit was not just a friendly phone call, but a clear signal of China's intention to deepen Arctic research, especially through expanded cooperation with Russia.
China's ambitions in the Arctic are not going unnoticed. In a defensive move, Norway recently blocked the sale of Søre Fagerfjord, a 60-square-kilometer property in Svalbard, listed for $326 million.
The Norwegian government's swift action was aimed at preventing China from acquiring the land under the 1920 Treaty of Svalbard, highlighting growing unease over China's Arctic aspirations.
The Yellow River flows north
At the heart of China's Arctic strategy is the Yellow River Station, established in 2003 in Ny-Ålesund, the world's northernmost civilian settlement. This research facility, focused on atmospheric studies, climate change and glaciology, serves as China's eyes and ears in the Arctic.
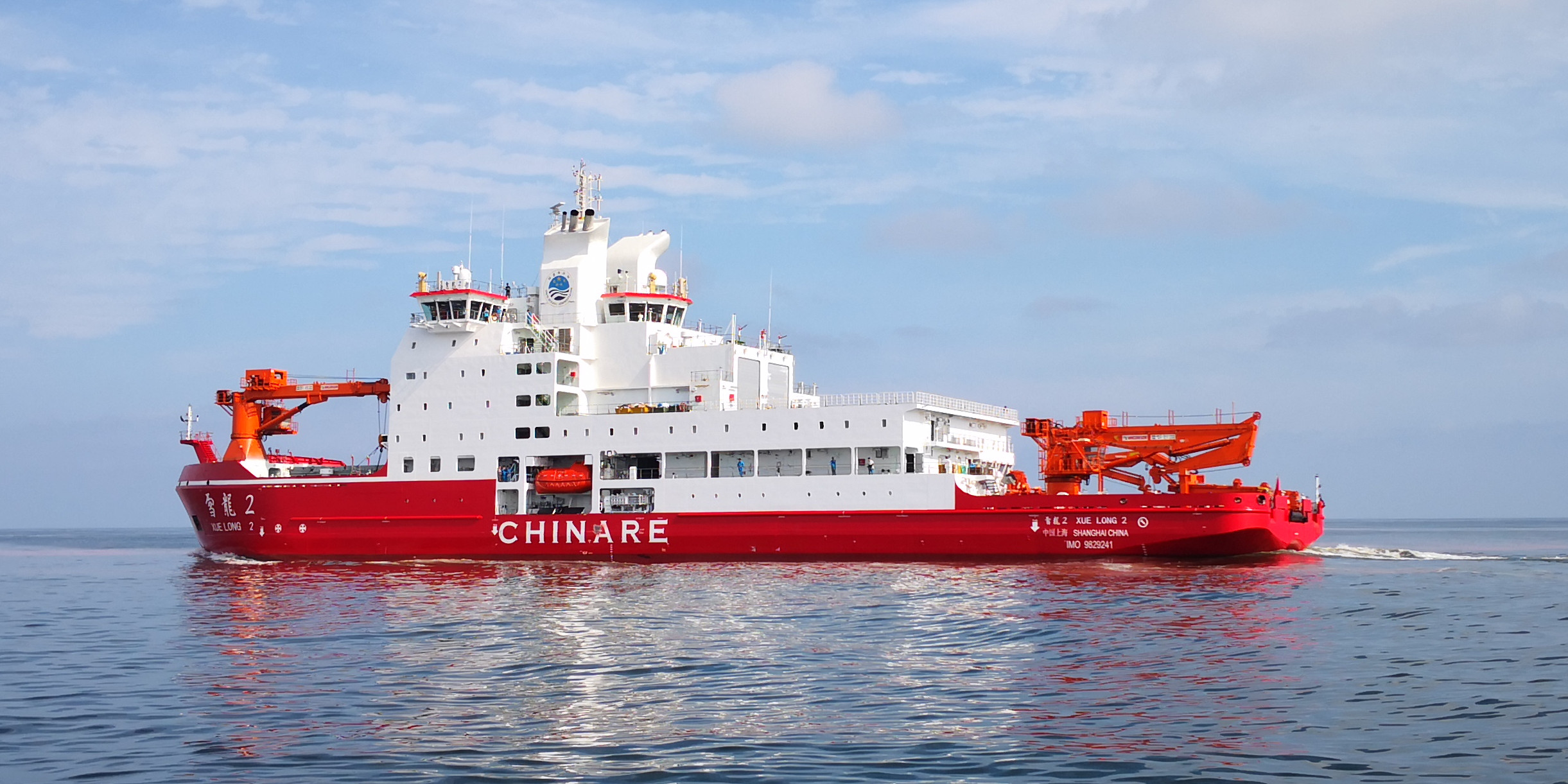
In 2023, China placed acoustic listening buoys in the North Sea and increased its research activities in Ny-Ålesund. This summer, China made an unprecedented move by deploying three icebreakers to the Arctic, including its most advanced vessel, the Xue Long 2.
These icebreakers are part of China's latest Arctic expedition, reflecting its growing interest in the region, especially cooperation with Russia on the Northern Sea Route (NSR).
China's scientific efforts in Svalbard are in line with its broader goal of deepening understanding of the Arctic environment and climate change. While this research contributes to global scientific knowledge, it also provides China with strategic insights that could influence its decisions in the region.
A crowded Arctic stage: China, Russia and Turkey
China is not the only player vying for influence in Svalbard.
Long known for its strategic location near the Arctic Ocean, Svalbard has recently attracted the attention of China, Turkey and Russia.
Over the past two months, these countries have sent research delegations to Svalbard, signaling their intent to collaborate on Arctic studies. Since 2023, Beijing and Moscow have been working together to develop the Northern Sea Route along Russia's Arctic coast.
Russia, with its long-standing presence in the region, has also flexed its muscles. In a controversial move last June, Russian state mining company Trust Arktikugol raised the Soviet flag in Svalbard, accompanied by the slogan “Peace to the World”.
Not to be left out in the cold, Turkey has also set its sights on Svalbard. The Turkish Arctic Science Expedition recently visited Pyramiden, a former mining town in Svalbard, proposing it as a site for an international Arctic station.
The strategic importance of Svalbard
Why all this interest in a remote and frozen archipelago?
Svalbard is an archipelago located north of mainland Norway. It is twice the size of Belgium and is located halfway between Norway and the North Pole. Its strategic location offers crucial access to key Arctic shipping routes, particularly the Northern Sea Route (NSR), which could dramatically reduce shipping distances between Europe and Asia.
As the Arctic ice melts, these routes are becoming more navigable, turning Svalbard into a key hub for Arctic shipping. Its proximity to Russia's northern territories and the resource-rich Barents Sea further amplifies its strategic value.
Furthermore, the archipelago is rich in coal, with a Norwegian and a Russian mine still active.
The Treaty of Svalbard
China's activities in Svalbard are framed in the context of the 1920 Svalbard Treaty.
Signed on 9 February 1920 in Paris, the Svalbard Treaty established Norwegian sovereignty over the strategically located archipelago between Norway and the North Pole after World War I. The treaty grants signatory countries, including Russia and China, equal rights to commercial activities in Svalbard, while affirming Norwegian sovereignty.
It guarantees all signatories and their citizens the same rights to exploit Norway's resources and establishes that no country may be treated differently on the basis of nationality. It is important to note that the treaty also demilitarized the region, prohibiting the permanent stationing of troops, including Norwegian ones.
Chinese threat
Some Nordic nations are increasingly concerned about the potential risks posed by China's activities in the Arctic, especially given its cooperation with Russia.
According to a recent report published by ' Svalbardposten ', the Norwegian Police Security Service (PST) has noticed an increase in Chinese interest in Svalbard.
Their 2024 National Threat Assessment highlights the presence of Chinese students and researchers in the archipelago, suggesting their activities could normalize Chinese influence and aid intelligence operations.
In recent years, China has also made several attempts to purchase Norwegian properties, including homes, cabins and commercial properties, and has expressed interest in establishing a laser station in Adventdalen.
Norway's counter move
China's expanding footprint in Svalbard and the Arctic is sparking unease among Arctic states, particularly regarding the risk of increased geopolitical competition and militarization.
NATO member Norway is at the forefront of these concerns. The NATO alliance is wary of the potential military uses of Russia and China's Arctic expansion.
In response to these growing threats, Norway has taken steps to regulate scientific activities in Svalbard. A new white paper aims to curb the creation of new research and education centers in the region, while the Svalbard Research Office proposal is designed to oversee and coordinate foreign study projects.
As Arctic ice continues to retreat, Svalbard's geopolitical heat is increasing. With China making bold moves, Russia reasserting its influence and NATO keeping watch, this remote archipelago has become a crucial player on the global stage.

Thanks to our Telegram channel you can stay updated on the publication of new Economic Scenarios articles.
The article China's attention reaches the remote Svanbard Islands comes from Economic Scenarios .
This is a machine translation of a post published on Scenari Economici at the URL https://scenarieconomici.it/lattenzione-della-cina-arriva-fino-alle-remote-isole-svanbard/ on Thu, 05 Sep 2024 15:52:26 +0000.